Defining the Ligand Network#
A LigandNetwork is a network where nodes are SmallMoleculeComponents and edges are LigandAtomMappings.
For example, a LigandNetwork with drug candidates as nodes can be used to conduct a free energy campaign and compute ligand rankings.
openfe includes an interface to common Network Planners, which are implemented in OpenFE’s konnektor package. (See konnektor’s documentation for more information on network generators.)
A LigandNetwork is constructed from SmallMoleculeComponent, which represent the nodes and optionally LigandAtomMapping, which represent the edges of the network.
A LigandAtomMapping can have a score associated with the mapping which can be used by some network generators to construct more efficient network topologies.
Below is an example of a LigandNetwork with scores assigned to each atom mapping:
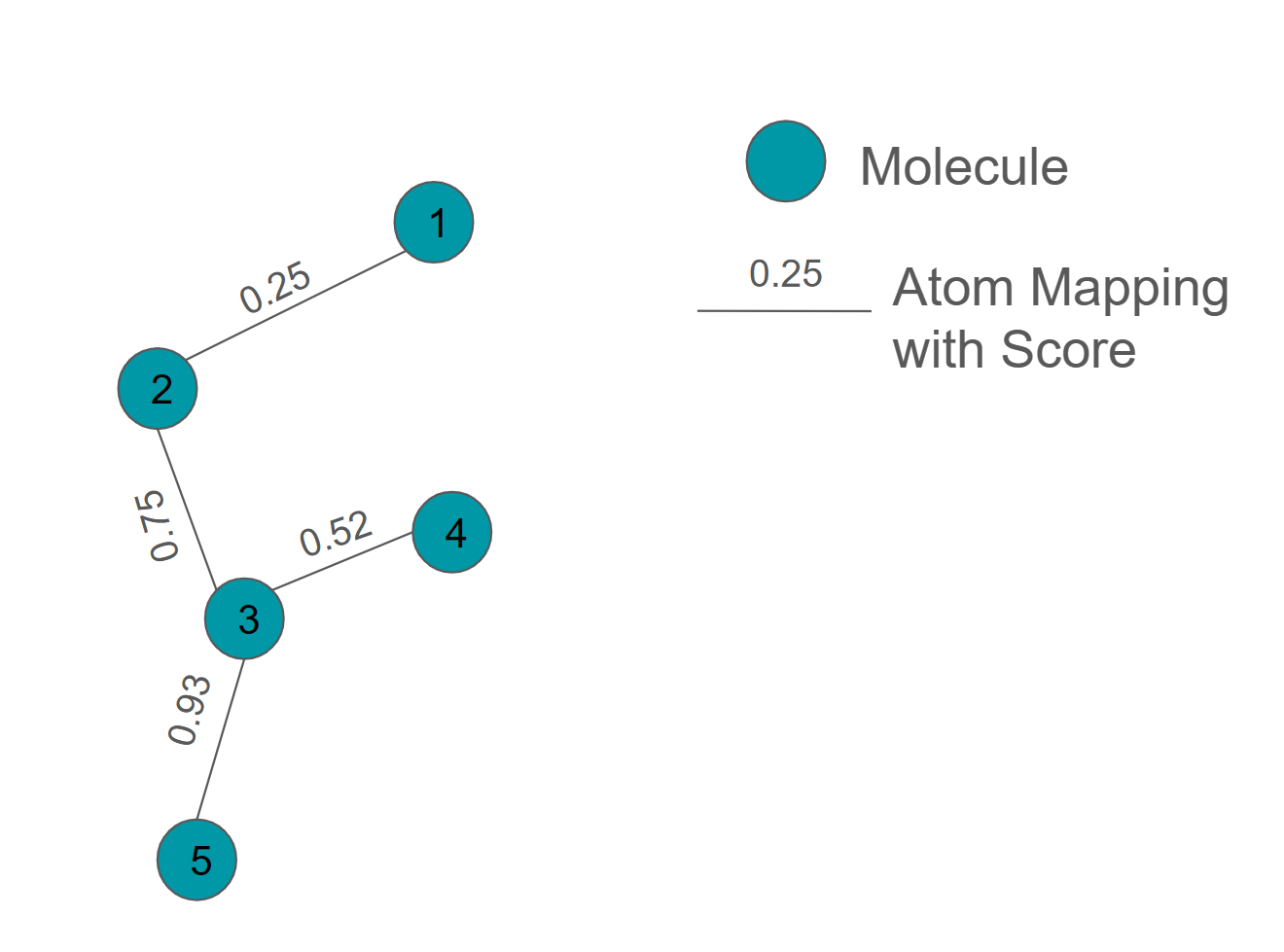
Generating Ligand Networks#
LigandNetwork generation can typically described by three steps:
Generate the Atom Mappings of all pairwise combinations of
SmallMoleculeComponentsCalculate scores for each
LigandAtomMappingBuild a
LigandNetworkwith all possible mappings directed by their scores.
import openfe
from openfe import setup
# load a set of ligands
mols = [SmallMoleculeComponent.from_rdkit(x) for x in rdmols]
# generate the required mapper, scorer, and planner objects
mapper = setup.KartografAtomMapper()
scorer = setup.lomap_scorers.default_lomap_score
network_planner = setup.ligand_network_planning.generate_minimal_spanning_network
# plan the ligand network
ligand_network = network_planner(ligands=mols, mappers=[mapper], scorer=scorer)
Practical information on generating ligand networks can be found in our cookbook for ligand network generation.
Note
Like the Component objects, a LigandNetwork object is immutable once created!